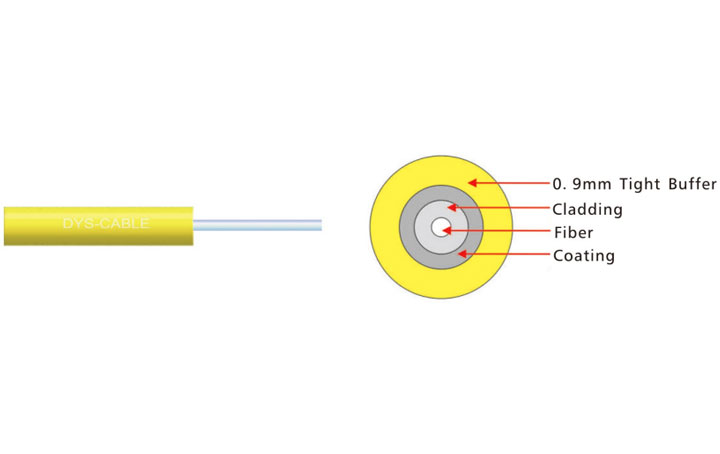
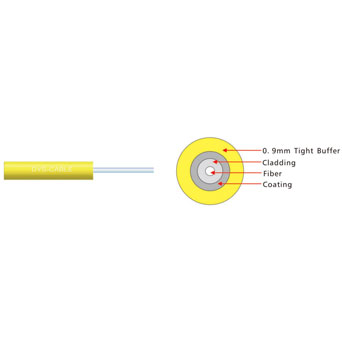
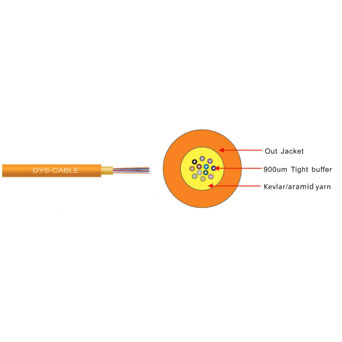
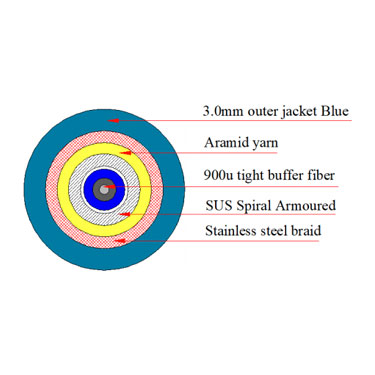
Construction and Durability:
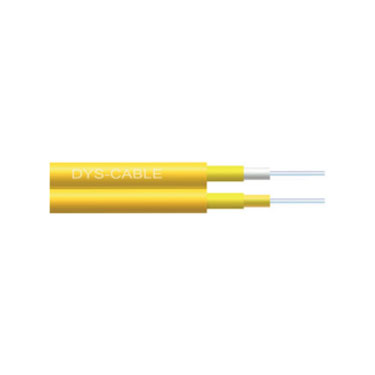
Indoor Fiber Cables: Designed for use inside buildings, with a focus on flexibility and ease of installation. They typically have a lighter, more flexible construction with a PVC or flame-retardant jacket.
Outdoor Fiber Cables: Built to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as UV radiation, moisture, and extreme temperatures. They often have stronger, weatherproof jackets made of materials like polyethylene and may include additional armoring for physical protection.
Protection Against Environmental Factors:
Indoor Fiber Cables: Primarily shielded from physical damage and are not designed for exposure to outdoor elements like rain or direct sunlight.
Outdoor Fiber Cables: Equipped with protective coatings or armoring to resist water, rodents, and other environmental hazards, making them suitable for burial or overhead installation.
Installation Environment:
Indoor Fiber Cables: Used in controlled environments such as offices, homes, and data centers, where environmental conditions are stable.
Outdoor Fiber Cables: Designed for use in more rugged and varied conditions, such as for underground, aerial, or direct burial installations.
Fire Resistance:
Indoor Fiber Cables: Often feature flame-retardant jackets for safety in case of a fire.
Outdoor Fiber Cables: May have additional fire resistance, but the primary concern is durability against external conditions.
Common types of indoor optical fiber cables include:
GJJV: General purpose fiber optic cable
GJFJV: Flame-retardant fiber optic cable
GJFJZY: Cable with a flame-retardant jacket
GJSJBV: Indoor fiber optic cable with a PVC outer sheath
GJFJBV: Flame-retardant cable with PVC sheath
GJSJV: General-purpose PVC cable
GJSJBV: High-quality PVC-coated fiber optic cable

 EN
EN